MCP: Real-time proteomics may speed cancer surgery
and her team are out to change surgical oncology. “Better surgery is associated with better prognosis and higher survival,” said Fournier, a professor at the and co-director of a proteomics center of , the French national institute of health. Her laboratory has worked for several years on a device they call the SpiderMass that will enable surgeons to look for markers of cancer in a living patient’s tissue, during an operation. in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, the team reports on an important step toward finding protein biomarkers during surgery.
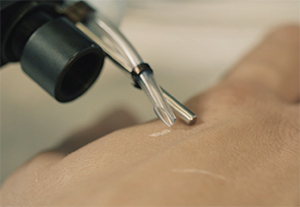 This photo shows in vivo analysis of the skin using the SpiderMass. The device leaves a white trail of dehydrated skin, but the traces disappear within a few minutes. COURTESY OF ISABELLE FOURNIER
This photo shows in vivo analysis of the skin using the SpiderMass. The device leaves a white trail of dehydrated skin, but the traces disappear within a few minutes. COURTESY OF ISABELLE FOURNIER
Surgery to remove a primary tumor involves a wait. After the tumor and some healthy surrounding tissue are removed, the surgical team pauses while a pathologist checks the tissue margins under a microscope. Although this process is important for preventing recurrence of the cancer, it can add up to 45 risky minutes under anesthesia.
With the new device, Fournier said, “We think that it is possible to open the way to in vivo real-time proteomics,” which could help surgeons find stray cancer cells faster, perhaps even as they make incisions.
Fournier’s device uses mass spectrometry, which measures the mass of molecules from complex mixtures. But turning an in vivo tissue sample into gas phase ions for measurements can be a challenge. Until now, no one knew how to extract ions from living tissues without doing harm.
So Fournier’s team got creative. Riffing on MALDI, an ionization strategy that uses a carrier molecule mixed with the analyte of interest, they decided to use the water that makes up a majority of human tissue as a carrier to produce a water-assisted laser desorption/ionization, or WALDI. If they could excite the water in a tiny area, it should vaporize, taking ionized organic molecules with it.
“It was an idea at the beginning, and many people thought that it would not work,” Fourier said. “Finally, we have it working beautifully.”
The team built a pulsed laser excitation device tuned to heat water precisely by causing vibration in the oxygen-hydrogen bond. In , they described using this laser to ionize the outermost layer of tissue, penetrating less than one-twentieth of a millimeter. The human volunteers reported a slight tingling sensation. But the ions that appeared were mostly small molecules and lipids, which are more apt than proteins to adopt a negative charge. The team hoped to measure proteins as well.
In this new paper, Fournier and colleagues report that they have cracked the protein puzzle. By using a more sensitive mass spectrometer and looking for positively instead of negatively charged ions, they found peaks representing purified proteins they had introduced into a cow liver sample. Now that they know the proteins are detectable, the next step will be finding ways to amplify the protein signal over more abundant lipids and metabolites.
In the meantime, the device is already in use for four-legged patients. Fournier’s lab has worked with the veterinary biotech company Oncovet Clinical Research to run a pilot trial, comparing biopsies from pet dogs with sarcoma to healthy tissues. The team developed a lipidomics- and metabolomics-based classification system to robustly identify healthy, necrotic and cancerous tissues. Soon, they will introduce a prototype into a veterinary operating room. If it is successful there, Fournier said, she hopes to reach human clinics, improving tumor removal surgery to give patients better health outcomes.
Enjoy reading 91Ó°żâToday?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from 91Ó°żâToday
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Hope for a cure hangs on research
Amid drastic proposed cuts to biomedical research, rare disease families like Hailey Adkisson’s fight for survival and hope. Without funding, science can’t “catch up” to help the patients who need it most.

Before we’ve lost what we can’t rebuild: Hope for prion disease
Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, a husband-and-wife team racing to cure prion disease, helped develop ION717, an antisense oligonucleotide treatment now in clinical trials. Their mission is personal — and just getting started.

Defeating deletions and duplications
Promising therapeutics for chromosome 15 rare neurodevelopmental disorders, including Angelman syndrome, Dup15q syndrome and Prader–Willi syndrome.

Using 'nature’s mistakes' as a window into Lafora disease
After years of heartbreak, Lafora disease families are fueling glycogen storage research breakthroughs, helping develop therapies that may treat not only Lafora but other related neurological disorders.

Cracking cancer’s code through functional connections
A machine learning–derived protein cofunction network is transforming how scientists understand and uncover relationships between proteins in cancer.

Gaze into the proteomics crystal ball
The 15th International Symposium on Proteomics in the Life Sciences symposium will be held August 17–21 in Cambridge, Massachusetts.

